
Now that you have a better overview of digital music (specific features, storage, etc.), we are going to outline the various playback possibilities that it can offer. Indeed, there are several devices that can play back your digital files: DAC, network player, audio server and computer/tablet. It is therefore possible to opt for several configurations according to your need.
As each device has its specific features, we thought it would be useful to provide information on their operation. The issue of quality also crops up frequently in digital music. We are therefore going to use the CD player as our base, a system known by everyone and that also uses digital media, to show what quality can be expected from our digital files.
DAC
The DAC (digital-to-analogue converter) is a the core of digital music as this device converts the digital signal into an analogue signal. As we have seen in the technical specifications for digital music, the human ear cannot detect a digital signal. This signal must therefore be converted into an analogue one to be heard by the human ear. This is where the DAC comes into play! The converter receives the digital signal coming from a digital source (computer, CD, file, server, etc.) to convert it into an analogue signal.
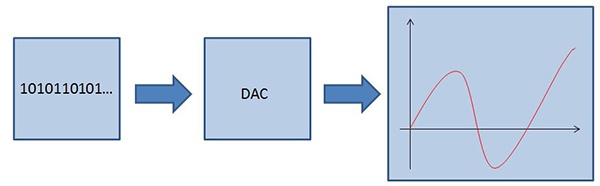
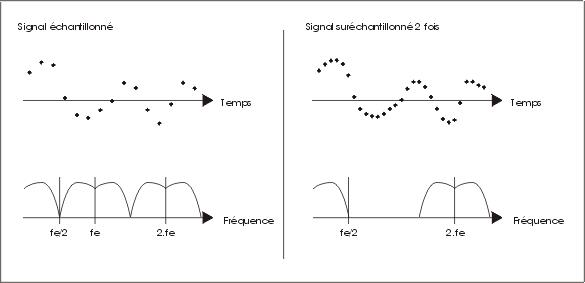
The analogue signal provides a representation that reflects the original signal. All digital files need to be converted into analogue. They are measured in bits (quantization) and sampling frequency (kHz). It is important to know that the higher the number of bits and sampling rate, the higher the quality obtained. Each DAC processes a specific sampling frequency of 32 kHz, 44.1 kHz, 48 kHz, 88.2 kHz, 96 kHz, 192 kHz to 384 kHz. The DAC can then artificially increase the sampling frequency of your source signal so as to considerably improve the sound quality. This is called over-sampling. The following is a graphic example:
There are 2 distinct types of DAC:
- Integrated DACs: Any digital source has an integrated DAC so as to be able to send music to your Hi-Fi system.
- External DACs: There are also units fully dedicated to digital-analogue conversion. They can therefore provide optimum sound quality of the source. We can use the example of a CD player: an external DAC associated with your CD player will override the internal DAC, so the CD player is used solely for transport (drive). We keep in mind that an external DAC can improve the sound quality of the source as the digital to analogue conversion will therefore be more precise.

Technologies:
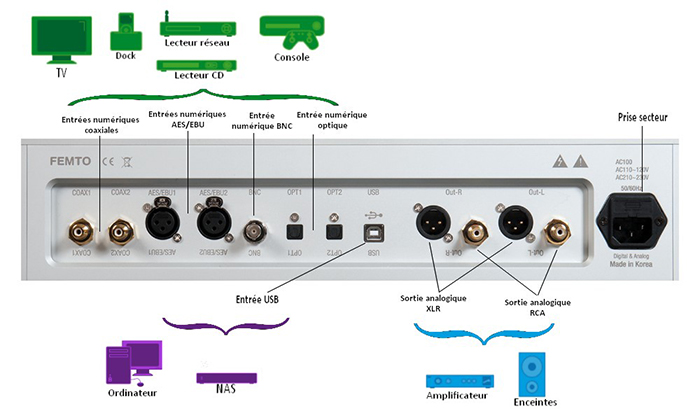
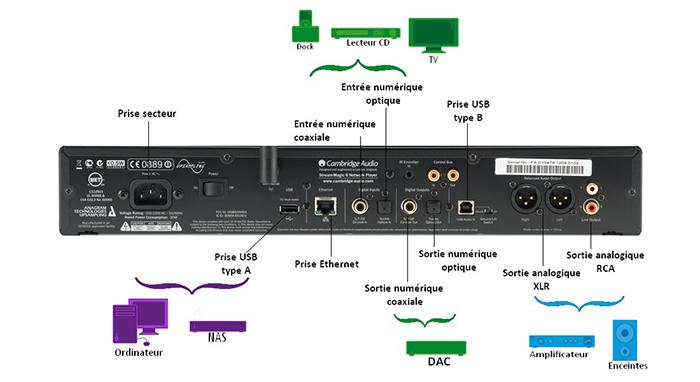
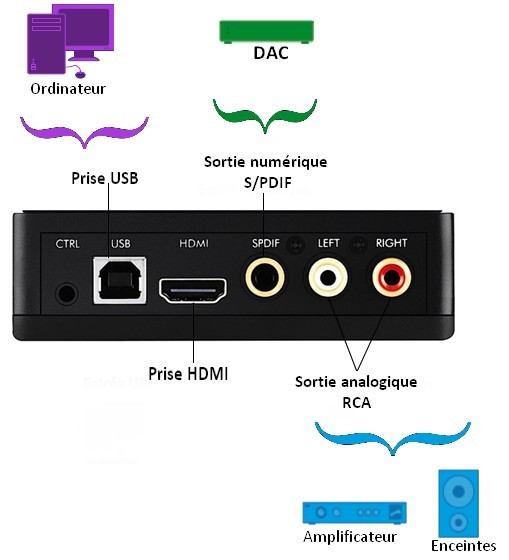
A DAC can have several types of connectors to adapt to various sources. Any audio system (computer, CD player, network player, audio server, etc.) can thus exceed its basic quality.
Inputs
A DAC can feature USB inputs, very useful for connecting your DAC to your computer (PC or Mac). This allows it to give your files the best possible sound quality. There are two types of USB transmissions:
- Synchronous USB (USB class 1): synchronous transmission is not considered to be optimum for audio listening. In this case, the computer's clock controls the transmission.
- Asynchronous (USB class 2): This is the most advanced mode. Here, the DAC controls the transmission and therefore the clock of the computer.
In addition to a USB input, the DAC can have a digital input for a perfect adaptation to any type of source (player, CD player, etc.). There are many types of digital inputs that are as follows:
- DAC with RCA coaxial digital input: used to connect sources that have RCA coaxial digital outputs.
- DAC with Toslink optical digital input: operates in relation with sources that have Toslink optical digital outputs.
- DAC with AES/EBU – XLR digital input: used to operate with sources that have an XLR digital output. This connector is used to connect cables of greater length without compromising the quality.
- DAC with BNC digital input: this connector is more frequently used in the professional world (studio, etc.).
Outputs
Several outputs can be presented on the DAC so as to connect it to several types of amplifiers:
- Asymmetric analogue output: RCA phono. The is the most common connector featuring on Hi-Fi devices.
- Symmetric analogue output: XLR. This connector is used to obtain greater gain and connect longer cables.
Here is an example of a DAC comprising all these connector types. All DAC are not necessarily equipped with them. Here we link the connectors as well as the devices that can be connected with them:
The DAC is therefore an essential element for playing your digital music, as it is the basis for processing the stream. Another element is very often used to play digital files in audiophile quality: the network player.
The network player
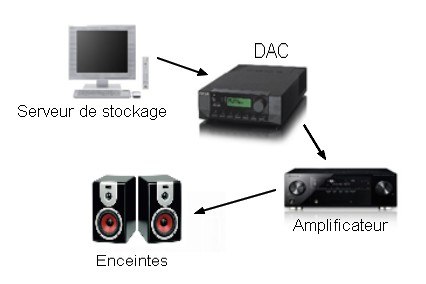
The role of the network player is to receive the digital file stored on your storage server (more information can be found in the fact sheet on digital music storage) in order to decode it. That is the digital file is converted into an audio stream, to enable the DAC (integrated or external) to convert it into an analogue signal. The network player can thus transmit the latter to the amplifier then to the speakers.
So as to go and look for the digital files of our musical library stored on your storage server, it is necessary that the network player has access to internet (as its name indicates, the player must be 'in the network'). The connection can be wired, that is Ethernet (thanks to the RJ45 sockets), or wireless, in other words Wi-Fi. Thanks to this connection, you can access all the world's web radios. Indeed, most of the radios we listen to over the waves also broadcast their programmes over the internet.
There are 2 solutions to control the network player. Indeed, some have an interface from which you can navigate between your playlists directly from the device. Others do not have this option, it is therefore necessary to have an external device (Smartphone, remote control, touch tablet, etc.).
Moreover, a network player does not have any storage server. It is therefore impossible for you to store your music library directly on it. You must therefore associated with an external storage server (different solutions are set out in the fact sheet on digital music storage).
Some are asking what is the usefulness of a network player if you have a computer that allows you to play your music library. In this case, the network player allows you to listen to your music library while being in another room than the one that contains your computer (which is used here as a storage server). Another advantage, if you have several computers, the player can then look for tracks on each computer in each room to play it on the same system.

Moreover, the use of a network player will provide a superior listening quality. We can use the CD player as our base, that plays the same types of files, namely, digital files. Indeed, the CD player can only play at the resolution and 16 bits/44.1 kHz sampling rate used on the CD. As for the network player, it has the ability to read several file formats (you can find out about the different audio file types by consulting the sheet regarding digital music), and therefore play superior quality formats.
Moreover, the very operation of the network player provides a better listening quality than that of the CD player. Indeed, the digital information burned on a CD is only read once by the CD player, which can sometimes miss its target and create an error, and thus requires a corrector to intervene. This reproduces a signal from information that it has already been able to recover. This entire procedure can therefore generate a temporal distortion called 'jitter'. To fully understand, we can say that the 'jitter' is to music what a blurred image is to cinema. Owing to the latter, it can be difficult for the DAC to reproduce the signal from the CD exactly in analogue form. In contrast, the network player can replay the information several times and store it in the 'buffer stage', which will reduce 'jitter'. Under these conditions, the network player can reproduce a better signal than the CD player and provide better quality music. You must naturally not forget to take into account the technological and internal elements comprising the network player (DAC, clock, etc.) when talking about quality.
Naturally, the sound quality will depend on the capacity of your network player to process the different types of existing formats. Some can read most formats whereas others will focus on better quality formats to give priority to an audiophile listening experience.
Technologies:
Depending on its internal technology, the network player can have different input types. Indeed, as we have seen before, the network player always has an integrated DAC.
In order to connect several sources to them, all the network players have USB inputs, coaxial, optical and AES/BU digital inputs. Naturally, you can learn more about connectors by going to the fact sheet dedicated to them.
On the contrary, some network players can comprise two DACs. The first is loaded from the conversion of the analogue signal coming from the storage server, whereas the second is useful for processing other digital sources that can be associated with the network player (CD player, TV, etc.). These network players contain all these types of connectors but they also feature Toslink optical and coaxial digital inputs.
Regarding outputs, all the network players have analogue outputs so that you can connect your amplifier to them.
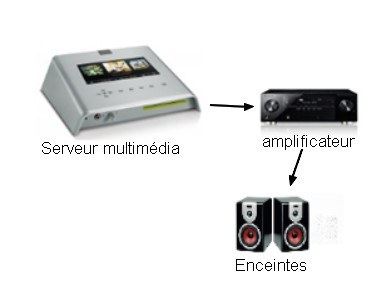
There is another system that can be substituted for the network player, this is the multimedia server.
Multimedia server
The multimedia server processes the audio stream in a similar way to the network player. Indeed, the latter can decode digital files to allow the DAC (like all sources, the multimedia server has its own internal DAC) to convert the audio stream into an analogue signal, so as to send it to your amplifier then the speakers.
In addition to its capacity to decode and convert digital files, the multimedia server can store them internally. You can therefore store your music library on this device, which means that the multimedia server comprises its own storage solution.
Moreover, the latter can rip your CDs (when you 'rip' a CD, you copy it directly onto a storage server). You will thus find them on the multimedia server and can listen to them from it.
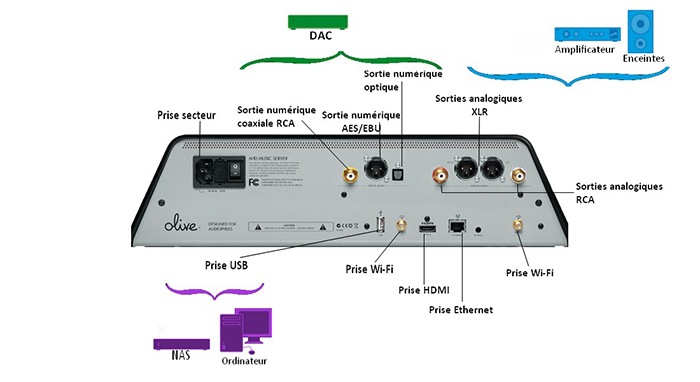
This implies being able to manage your music library directly from the device. Indeed, in contrast with the network player, the multimedia server necessarily features an interface to allow you to navigate between the tracks of your music library.
The audio server has another advantage from its integrated storage server: it enables it not to depend on an internet connection. Indeed, you can directly store your music library on it by ripping your CDs (most audio servers have a CD player) or by inserting a USB key. However, you will need an internet connection if you want to import digital files remotely from your computer.
Consequently, the multimedia server is a device that can function autonomously. It can be advantageous if you do not want to multiply devices: the latter can operate very well only in relation to an amplifier and speakers.
As the operation of the network player and audio server are similar in several ways, we can say that the music quality that they can produce depends on the same specific features. Indeed, the quality will depend on the type of formats that the multimedia server can process (depending on its integrated DAC). Moreover, its internal operation is similar to that of the network player. That is, it also uses a 'buffer stage' that enables the digital data to be stored so as to reprocess them in the event of a playback error.
Technologies:
Like the network player, the multimedia server can have several inputs and outputs.
Regarding outputs, it can have digital data so as to be able to add to it an external DAC to increase its audio performances. Moreover, very often, the device has a USB input. This input makes it possible to transfer your music library via a USB drive if you do not have an internet access for example.
The multimedia server necessarily has analogue outputs that can be, here too, RCA or XLR, with the aim of connecting to your Wi-Fi system.
Computer
Another solution is open to you for listening to digital music. Indeed, the mechanics of a computer allows it both to read and store your music library. Here, it is the sound card of your computer that will process the digital file to send an analogue signal to speakers integrated with it.
So as to transmit your digital music to your Hi-Fi system (amplifier + speakers), you need to associate a DAC external to your computer. Hence, you can benefit from a very high playback quality by using a high-end DAC.
The advantage of such a system is its upgrade capacity by changing the DAC, PC or playback software. However, the computer must always be situated near your Hi-Fi system and also with the power continuously on.
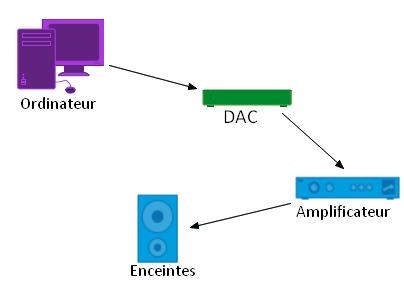
Technologies:
A computer has two main types of outputs:
- A USB output that can add a USB external DAC
- This connection can be done via 3.5 jack – RCA, 3.5 jack – 3.5 jack or optical 3.5 jack, more often used by Mac computers.
Tablet, Smartphone, iPod, USB drive
The latest solution that we see for the playback of your digital music is the use of an Ipod, Iphone or a touch tablet. Just like the computer, they can store, play and send music using their internal operation.
However, to get the best out an audiophile recovery, it is recommended to associate it with a dock. The Smartphone is thus used as a storage server and the dock is the player. The advantage of the Dock is that it can very often recharge your device.
Two kinds of Dock can be differentiated. The first type is the amplified dock, that can operate autonomously. Indeed, it comprises the amplifier and the speakers and can therefore play music for you. The other solution is a dock that is not amplified, that must be associated with your Hi-Fi system, namely amplifier and speaker.
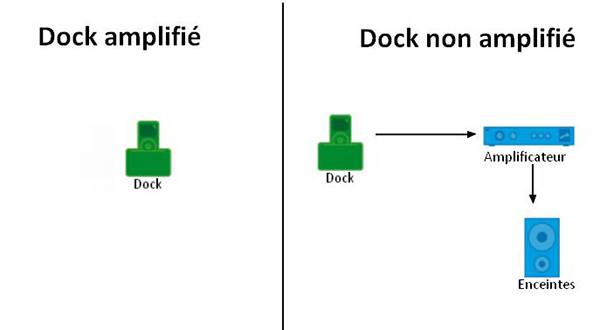
Technologies
Almost all Docks have an Ipod dock so as to be able to insert the Ipod, Iphone or tablet. Moreover, some Docks have a USB output as they are powered by a USB socket. A USB output can also be useful to add a DAC external to the device.
Non-amplified Docks have analogue outputs so as to connect them to a Hi-Fi system.
This part thus resumes all the options enabling the digital music to be played back. In a second part, you will find the different Internet connections as well as diagrams summarising the possible combinations with the level of listening that you can remove it.
![How do I choose a turntable ?]() How do I choose a turntable ? Discover
How do I choose a turntable ? Discover![How do I take care of my records?]() How do I take care of my records? Discover
How do I take care of my records? Discover![The different types of Hi-Fi cables and their role]() The different types of Hi-Fi cables and their role Discover
The different types of Hi-Fi cables and their role Discover![How to choose your Hi-Fi speakers?]() How to choose your Hi-Fi speakers? Discover
How to choose your Hi-Fi speakers? Discover![How do you choose the amplifier?]() How do you choose the amplifier? Discover
How do you choose the amplifier? Discover![How do you choose your dematerialized equipment?]() How do you choose your dematerialized equipment? Discover
How do you choose your dematerialized equipment? Discover![How to place your Hi-Fi devices?]() How to place your Hi-Fi devices? Discover
How to place your Hi-Fi devices? Discover![How to build a complete Hi-Fi system?]() How to build a complete Hi-Fi system? Discover
How to build a complete Hi-Fi system? Discover






















